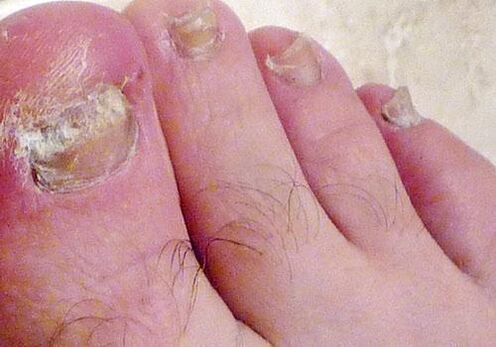
Onychomycosis is a disease of the nails of the hands and feet, caused by representatives of the fungal microflora, which gradually leads to the destruction of the nail plate with a change in its structure, color, shape.
The causative agents of onychomycosis include three types of fungi:
- Dermatomycetes. Dermatomycetes are parasitic fungi, the main representatives of which are Trichophyton, Microsporum, Epidermophyton. In 80-85% of cases, it is the dermatomycetes that become the source of the nail fungus.
- Fungi of the genus Candida (similar to yeast). The Candida fungus is present in the microflora of any human body, however, by its nature, it can begin to multiply rapidly, resulting in the formation of nail fungus. Candida fungus infects the nail surface in 8-10% of cases.
- Moldy. Molds are the rarest possible causative agents of nail fungus; they become infected only in 5-6% of cases.
Causes of nail fungus
In 100% of cases, onychomycosis occurs as a result of damage to the skin by fungal pathogens. Contact of the skin of the foot with the infected surface leads to the penetration of the fungus through the upper layers of the epithelium into the nail and, as a result, to further deformation of the nail plate. Depending on the location of the lesion, the following types of onychomycosis are possible:
- The fungus enters the nail bed through the surface of the nail edge. Since it is almost asymptomatic in the first few days of infection, it is difficult for the patient to notice any changes. But when the fungus grows right in the nail bed, hyperkeratrosis begins to develop. Hyperkeratrosis is caused by a change in the color of the nail from light pink to yellowish, the connection between the nail surface and the nail bed is also weakened, which leads to delamination, peeling.
- The fungus can enter the nail through the free surface of the nail plate. This occurs when the spores have a high keratolytic capacity (rapidly destroying the keratin). In this case, the nail infection occurs much faster than in the first option.
- Through the nail fold (skin area adjacent to the nail plate). It is somewhat less common, however, with this method of infection, the inflammatory process of the nail matrix (root zone) can begin.
Risk factors that can lead to fungal nail infections
- flat feet or other features of the structure, development of the foot;
- varicose veins of the legs;
- decreased immunity due to previous diseases;
- HIV infection;
- increased sweating;
- wearing shoes and clothing made of synthetic materials;
- Low foot ventilation. It occurs again due to uncomfortable and tight shoes;
- mechanical damage to the foot;
- scratches, abrasions, open wounds;
- self-removal of an ingrown toenail;
- frequent use of antibiotics;
- candidiasis diseases (mainly in women);
- comorbidities. Diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders, dermatological diseases, stomach diseases, pancreas, excess weight can also increase the risk of onychomycosis up to 6-8 times;
Well, besides these factors, there are also ways through which you can be directly infected with nail fungus.
- Use of general personal hygiene items (pumice stone, wipes, slippers, flip flops)
- Visiting public saunas, baths, swimming pools, changing rooms without shoes.
- Put on someone else's shoes
- Failure to comply with sterilization standards in beauty salons (especially pedicures).
Symptoms, forms of onychomycosis
Symptoms of the disease depend on many factors: age, form of onychomycosis, degree of infection, state of the body as a whole. Symptoms of nail fungus infection are accompanied by itching, burning and skin irritation.
Currently, dermatologists distinguish five main forms of nail fungus damage:
- Hypertrophic. It is characterized by a strong thickening of the nail plate. The thickness of the nail can exceed 3-4 mm - this is due to an increase in small skin scales that grow on the infected surface of the nail. The lateral parts of the nail plate are subject to maximum destruction; the central (central) part, on the contrary, thickens. At the edges, the nail begins to crumble strongly. Due to hypertrophic damage, the nail becomes curved, narrow and very thick. In addition, there is a sharp change in the color of the nail, accompanied by peeling.
- Normotrophic. It is the simplest form, since the nail, when hit by the fungus, does not thicken, but remains the same. Only the color of the nail plate changes. The fungus begins with the appearance of a small yellow speck, which then rapidly grows in size. If you do not consult a specialist and start treatment, over time the stain will increase in size, gradually capturing the entire area of the nail plate. Since a person can quickly detect a color change, nail fungus can be diagnosed at a fairly early stage of the disease.
- Atrophic (onycholitic). The atrophic form of onychomycosis is accompanied by a sharp change in the color of the nail from pink to gray, with the subsequent destruction of the nail structure. Characterized by rapid progression, which ultimately leads to the complete detachment of the nail plate from the nail bed. In other words, the patient may accidentally hook or detach the infected nail and "remove" it completely. The final stage of the atrophic fungus is necrosis of the nail tissue.
- Lateral and distal. The lateral form is often diagnosed in combination with the distal type of fungus. The symbiosis of these varieties leads to a discoloration of the nail plate, starting with the appearance of yellowish longitudinal grooves, followed by an increase in the area of the nail lesion. Within 4-5 weeks, in the absence of proper treatment, the cells of the nail begin to die and the nail itself strongly crumbles. The final stage of lateral nail injury by a fungus is a complete exposure of the nail bed, which is dangerous with the risk of infection on the mucous membrane.
- Total form of onychomycosis. The total nail fungus is the lack of treatment for any of the above types of onychomycosis. Please note that the nail changes color very quickly, exfoliates, crumbles and then completely rejects from the nail bed. In this case, it is necessary to consult not only a dermatologist, but also a surgeon.
Phases of onychomycosis
To avoid getting infected with toenail fungus, it is important to remember that infection, as well as subsequent deformation of the nail, never occur overnight. In medical terms, this is the primary lesion, the normotrophic stage and the hypertrophic stage of the disease.
In the initial stage, the nail is only interested in the edges; at the same time, the size of the affected area does not exceed 2-3 mm. In rare cases, the free edge of the nail may be affected. Before direct damage to the nail, the skin of the feet becomes infected. The patient feels itching, rubbing and corns, painful corns may appear. Over time, the fungus passes from the foot to the nail. If you notice any changes at this point and consult a specialist, there is a chance to fully preserve and restore the nail plate in a short time.
The normotrophic phase is the next phase of the disease. An intermediate process in which the thickening of the nail plate has not yet begun, but the affected areas of the nail are already noticeable. The affected areas can be small (2-4 mm) or they can reach larger dimensions (more than 5 mm). Most often they are expressed in the form of thin vertical stripes with a yellowish tinge. The first manifestation of toenail fungus is the change in color: it can be noticed quickly and the treatment can be started in time.
The final stage of onychomycosis is the hypertrophic stage of the disease. It starts with the formation of a small speck under the nail, which then grows very quickly. It can be accompanied by an inflammatory process that goes in parallel with the formation of purulent sacs. The nail plate thickens, crumbles, exfoliates, then sharply becomes thinner, and, finally, the cells of the nail die and its complete exfoliation.
Important: The danger of hypertrophic nail damage also lies in the possibility of damage to the nearby skin and in the transition to a chronic plan. But such a development of events is possible only in the absence of timely medical intervention and subsequent treatment of nail fungus.
Treatment against nail fungus
The most popular are various antifungal drugs. The mechanism of action of such drugs is reduced not only to the destruction of direct spores, but also to the accumulation of the active substance in the nail plate itself. This avoids relapses and protects the legs from possible future injuries.
Before choosing one or another drug, it is absolutely necessary to pass a microbiological culture with the identification of the type of nail fungus, undergo a full diagnosis and consult a dermatologist.
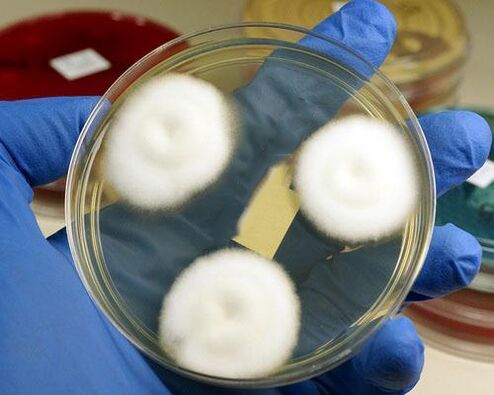
In the most modern dermatological clinics the following methods are used to diagnose onychomycosis:
- KOH microscopy
- High precision PCR diagnostics
A dermatologist, before prescribing a specific medicine, must take into account the nature of the fungal infection, the type of onychomycosis, the time elapsed from the moment of infection and much more.
The most commonly used methods of treatment: drugs, lasers and traditional medicine.
Medication
Among the antifungal drugs, the most popular are paints, ointments and tablets.
In the initial stages of the fungus, the use of topical preparations is recommended, among which antifungal paints occupy an important place.
Important: if a doctor has prescribed an antifungal varnish, the procedures should never be skipped, otherwise there will be no desired effect.
In addition to paints, there are also special ointments and gels that have the same antifungal effect. Ointments also belong to topical preparations. Most often, experts prescribe ointments. The ointment should be applied to the affected areas of the nail and foot for a period of time. The exact time of treatment is prescribed by a specialist.
There are also antifungal pills. Unlike ointments and varnishes, tablets are general-purpose medications that are taken orally. The most commonly prescribed antifungal pills are: Tablets are often prescribed not in the early stages of infection, but later, when the fungus has already entered the normotrophic stage.
Laser treatment against fungi
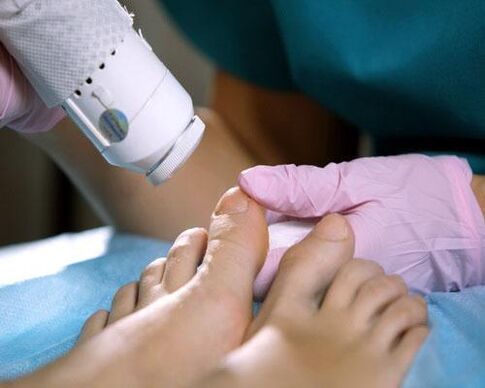
Currently, some clinics offer hardware treatment of nail fungus using a laser. Penetrating the subungual surface, the laser beam heats it up to the growth zone, not only killing the fungus, but also stimulating the growth of a new nail. Research by scientists has shown that with systematic heating of the nail plate to a temperature of 60-70 degrees, fungal microorganisms die. A similar thermal effect without damaging the surrounding tissues can only be achieved with the help of laser radiation, since the laser beam has a length that reacts only to cells affected by mycosis. Despite the fact that the method of laser exposure to the lesion promises the complete elimination of nail fungus, dermatologists, as a rule, recommend several sessions of such treatment. Compared to drug therapy, this method is much more expensive and therefore not suitable for everyone.
And for those who are too lazy to see a doctor, there are remedies from the arsenal of traditional medicine
Experts advise to resort to folk methods exclusively in combination with the ongoing traditional systemic treatment. Such funds can be used as preventive measures to eliminate the likelihood of recurrence of the fungus in the future.
Here are some recipes, the effectiveness of which in the treatment of nail fungus is likely, but not entirely necessary. However, in the absence of other opportunities to combat nail fungus, it is not forbidden to use these simple recommendations.
- Affected areas of the nail plate are treated with 5% iodine solution twice a day. When applying iodine, a slight tingling and burning sensation may be felt. If the discomfort intensifies, such treatment should be stopped and other treatment methods used.
- A 20% tincture consists of propolis, which is then applied to the areas of the skin and nails affected by the fungus. The action of propolis is to promote the rapid regeneration of damaged cells and the restoration of the nail. The effect of propolis becomes evident after a few applications.
- One of the best known ways to fight fungi alone is to use kombucha. To prepare a compress, you need to cut a small piece of ripe kombucha, use a bandage or gauze bandage to tie the fungus to the affected nail and leave it overnight. In the morning, unfasten the bandage and remove dead nail particles. Next, it is necessary to treat the affected area and the surrounding skin with an iodine solution or any other disinfectant. It is recommended to continue working the nail with kombucha for 3-4 weeks.
Prevention of fungal nail infections
- Any disease, including nail fungus, is easier to prevent than to cure. To protect yourself from nail fungus and minimize the risk of infection, you should follow simple preventative measures that will help you stay healthy.
- First of all, it is the observance of personal hygiene, especially in public places. This also applies to your apartment and even more so for public places like saunas and bathrooms. You should always wear individual slippers, use your loofah and pumice stone for heel care.
- If you notice excessive sweating of your feet, you should change your shoes or use special cooling insoles. These insoles have a porous structure, thanks to which they normalize air circulation.
- Regularly inspect your feet for micro cracks, scrapes and cuts. If scratches are detected, it is necessary to treat the place with antiseptics (alcohol solution of iodine and others).
Toenail fungus, like many other diseases, may not appear immediately, so it is very important to monitor the condition of the nails and skin of the feet. And it is better to carefully follow all prescribed preventive measures - these simple actions in the future will save time and money spent on treatment.






























